Deploying Turborepo to Vercel
Turborepo is a high-performance build system for JavaScript and TypeScript codebases with:
- Fast incremental builds
- Content-aware hashing, meaning only the files you changed will be rebuilt
- Remote Caching for sharing build caches with your team and CI/CD pipelines
And more. Read the Why Turborepo docs to learn about the benefits of using Turborepo to manage your monorepos. To get started with Turborepo in your monorepo, follow Turborepo's Quickstart docs.
Follow the steps below to deploy your Turborepo to Vercel:
It's important to ensure you are managing environment variables (and files outside of packages and apps) correctly.
If your project has environment variables, you'll need to create a list of them in your
turbo.jsonso Turborepo knows to use different caches for different environments. For example, you can accidentally ship your staging environment to production if you don't tell Turborepo about your environment variables.Frameworks like Next.js inline build-time environment variables (e.g.
NEXT_PUBLIC_XXX) in bundled outputs as strings. Turborepo will automatically try to infer these based on the framework, but if your build inlines other environment variables or they otherwise affect the build output, you must declare them in your Turborepo configuration.You can control Turborepo's cache behavior (hashing) based on the values of both environment variables and the contents of files in a few ways. Read the Caching docs on Turborepo for more information.
envandglobalEnvkey support is available in Turborepo version 1.5 or later. You should update your Turborepo version if you're using an older version.The following example shows a Turborepo configuration, that handles these suggestions:
turbo.json{ "$schema": "https://turborepo.com/schema.json", "pipeline": { "build": { "dependsOn": ["^build"], "env": [ // env vars will impact hashes of all "build" tasks "SOME_ENV_VAR" ], "outputs": ["dist/**"] }, "web#build": { // override settings for the "build" task for the "web" app "dependsOn": ["^build"], "env": ["SOME_OTHER_ENV_VAR"], "outputs": [".next/**", "!.next/cache/**"] } }, "globalEnv": [ "GITHUB_TOKEN" // env var that will impact the hashes of all tasks, ], "globalDependencies": [ "tsconfig.json" // file contents will impact the hashes of all tasks, ] }In most monorepos, environment variables are usually used in applications rather than in shared packages. To get higher cache hit rates, you should only include environment variables in the app-specific tasks where they are used or inlined.
Once you've declared your environment variables, commit and push any changes you've made. When you update or add new inlined build-time environment variables, be sure to declare them in your Turborepo configuration.
If you haven't already connected your monorepo to Turborepo, you can follow the quickstart on the Turborepo docs to do so.
Create a new Project on the Vercel dashboard and import your Turborepo project.
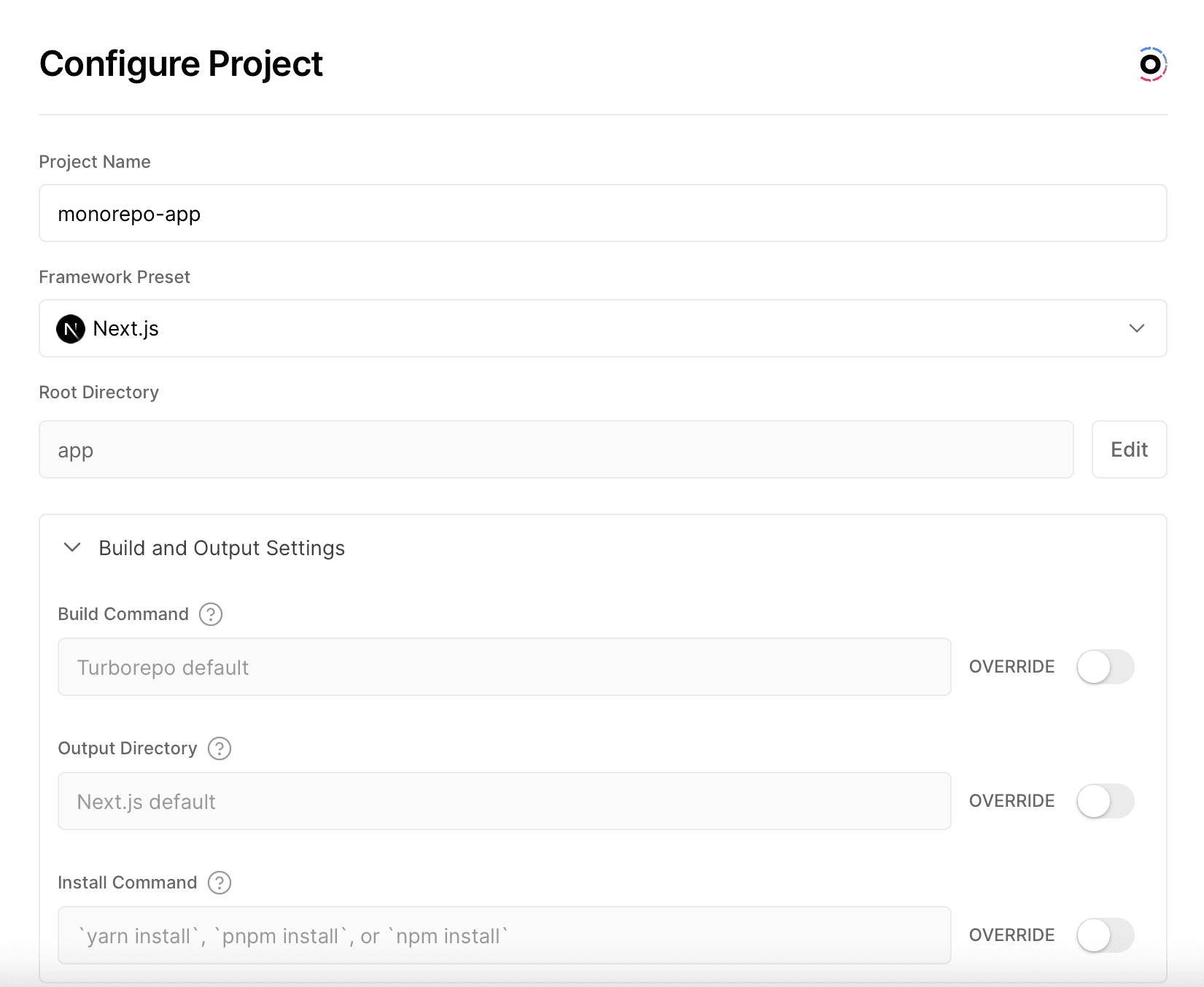
Configuring Project settings during import, with defaults already set. Vercel handles all aspects of configuring your monorepo, including setting build commands, the Output Directory, the Root Directory, the correct directory for workspaces, and the Ignored Build Step.
The table below reflects the values that Vercel will set if you'd like to set them manually in your Dashboard or in the
vercel.jsonof your application's directory:Field Command Framework Preset One of 35+ framework presets Build Command turbo run build(requires version >=1.8) orcd ../.. && turbo run build --filter=webOutput Directory Framework default Install Command Automatically detected by Vercel Root Directory App location in repository (e.g. apps/web)Ignored Build Step npx turbo-ignore --fallback=HEAD^1
Turborepo is also available globally when you deploy on Vercel, which means that you do not have to add turbo as a dependency in your application.
Thanks to automatic workspace scoping and globally installed turbo, your build command can be as straightforward as:
turbo buildThe appropriate filter will be automatically inferred based on the configured root directory.
To override this behavior and use a specific version of Turborepo, install the
desired version of turbo in your project. Learn
more
You likely don't need to build a preview for every application in your monorepo on every commit. To ensure that only applications that have changed are built, ensure your project is configured to automatically skip unaffected projects.
You can optionally choose to connect your Turborepo to the Vercel Remote Cache from your local machine, allowing you to share artifacts and completed computations with your team and CI/CD pipelines.
You do not need to host your project on Vercel to use Vercel Remote Caching. For more information, see the Remote Caching doc. You can also use a custom remote cache. For more information, see the Turborepo documentation.
First, authenticate with the Turborepo CLI from the root of your monorepo:
Terminalpnpm dlx turbo loginThen, use
turbo linkto link your Turborepo to your remote cache. This command should be run from the root of your monorepo:Terminalpnpm dlx turbo linkNext,
cdinto each project in your Turborepo and runvercel linkto link each directory within the monorepo to your Vercel Project.As a Team owner, you can also enable caching within the Vercel Dashboard.
Your project now has the Remote Cache linked. Run
turbo run buildto see the caching in action. Turborepo caches the filesystem output both locally and remote (cloud). To see the cached artifacts opennode_modules/.cache/turbo.Now try making a change in a file and running
turbo run buildagain. The build speed will have dramatically improved. This is because Turborepo will only rebuild the changed files.To see information about the Remote Cache usage, go to the Artifacts section of the Usage section in the sidebar.
For Vercel to deploy your application, the outputs need to be present for your Framework Preset after your application builds. If you're getting an error that the outputs from your build don't exist after a cache hit:
- Confirm that your outputs match the expected Output Directory for your Framework Preset. Run
turbo buildlocally and check for the directory where you expect to see the outputs from your build - Make sure the application outputs defined in the
outputskey of yourturbo.jsonfor your build task are aligned with your Framework Preset. A few examples are below:
{
"$schema": "https://turborepo.com/schema.json",
"pipeline": {
"build": {
"dependsOn": ["^build"],
"outputs": [
// Next.js
".next/**", "!.next/cache/**"
// SvelteKit
".svelte-kit/**", ".vercel/**",
// Build Output API
".vercel/output/**"
// Other frameworks
".nuxt/**", "dist/**" "other-output-directory/**"
]
}
}
}Visit the Turborepo documentation to learn more about the outputs key.
When using Turborepo on Vercel, all information used by turbo during the build process is automatically collected to help debug cache misses.
Turborepo Run Summary is only available in Turborepo version 1.9 or later.
To upgrade, use npx @turbo/codemod upgrade.
To view the Turborepo Run Summary for a deployment, use the following steps:
- From your dashboard, select your project and open Deployments in the sidebar.
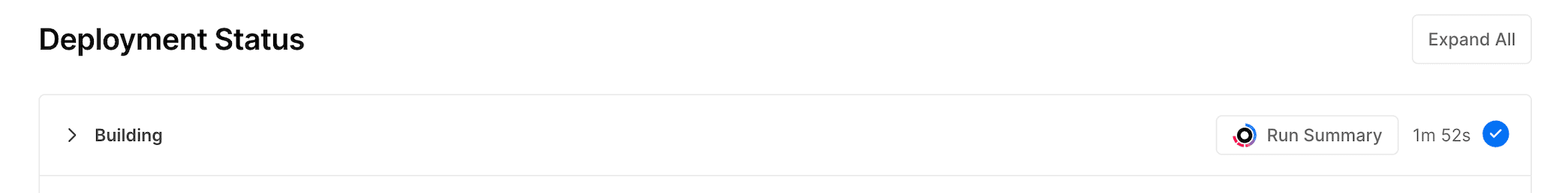
- Select a Deployment from the list to view the deployment details
- Select the Run Summary button to the right of the Building section, under the Deployment Status heading:

This opens a view containing a review of the build, including:
- All tasks that were executed as part of the build
- The execution time and cache status for each task
- All data that
turboused to construct the cache key (the task hash)
If a previous deployment from the same branch is available, the difference between the cache inputs for the current and previous build will be automatically displayed, highlighting the specific changes that caused the cache miss.
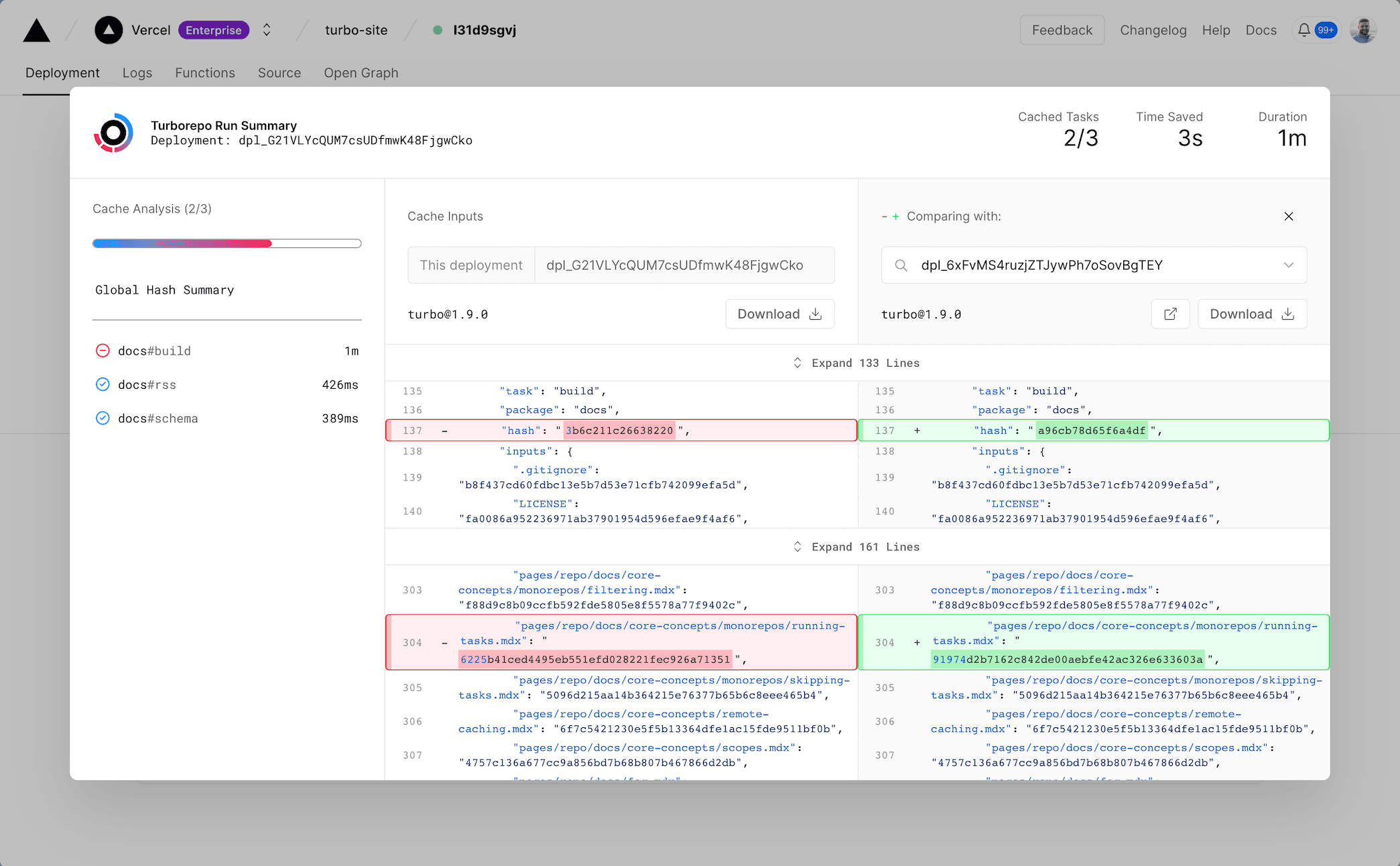
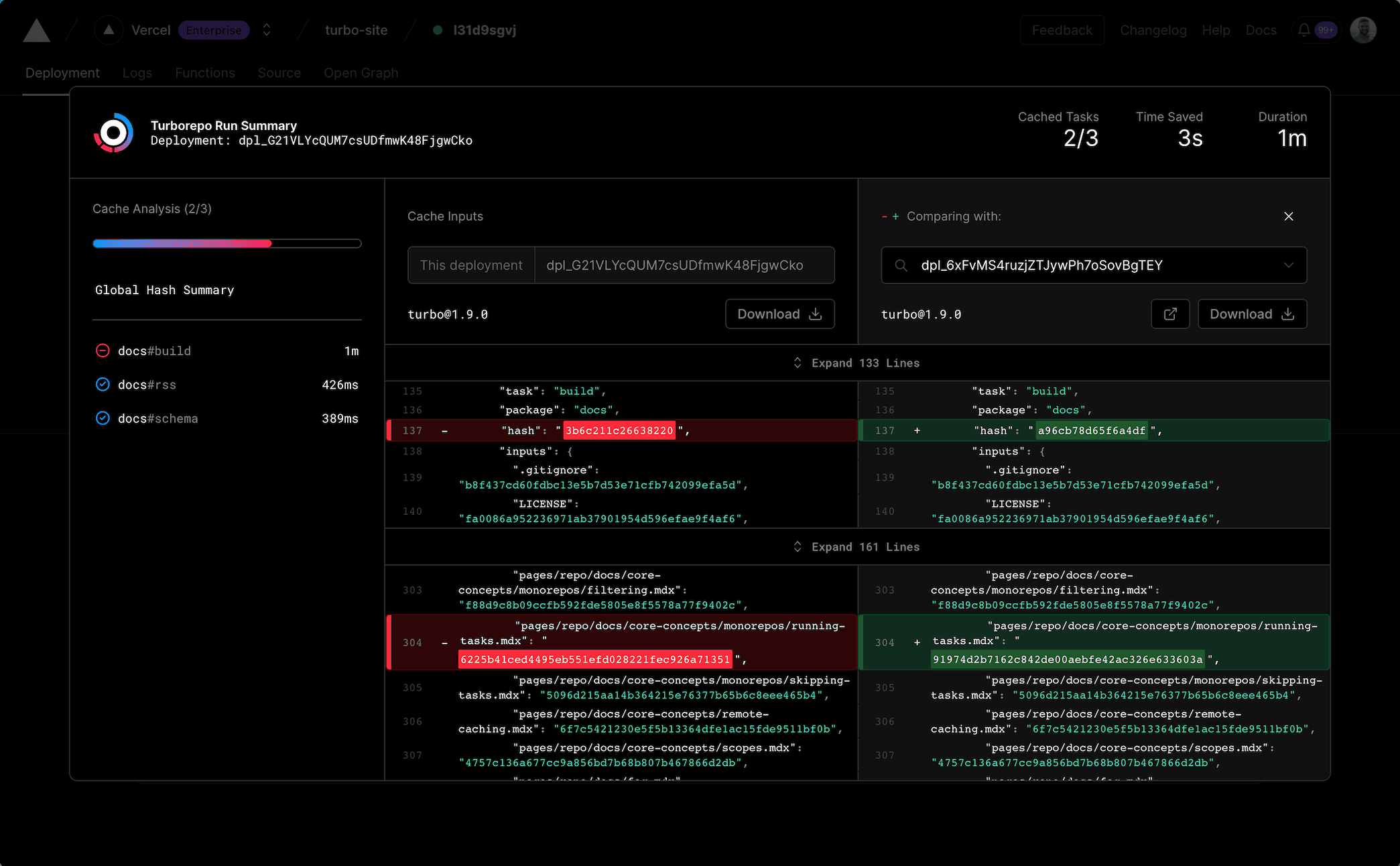
This information can be helpful in identifying exactly why a cache miss occurred, and can be used to determine if a cache miss is due to a change in the project, or a change in the environment.
To change the comparison, select a different deployment from the dropdown, or search for a deployment ID. The summary data can also be downloaded for comparison with a local build.
Environment variable values are encrypted when displayed in Turborepo Run Summary, and can only be compared with summary files generated locally when viewed by a team member with access to the projects environment variables. Learn more
Building a Next.js application that is using Skew Protection always results in a Turborepo cache miss. This occurs because Skew Protection for Next.js uses an environment variable that changes with each deployment, resulting in Turborepo cache misses. There can still be cache hits for the Vercel CDN Cache.
If you are using a version of Turborepo below 2.4.1, you may encounter issues with Skew Protection related to missing assets in production. We strongly recommend upgrading to Turborepo 2.4.1+ to restore desired behavior.
Was this helpful?

