Deploying from Azure DevOps with Vercel
The Vercel Deployment Extension allows you to automatically deploy to Vercel from Azure DevOps. You can add the extension to your Azure DevOps Projects through the Visual Studio marketplace.
This flow is commonly used to deploy to Vercel projects from a codebase hosted in Azure Repos, but it can be used with any Git repository that can integrate with Azure Pipelines.
Once the Vercel Deployment Extension is set up, your Azure DevOps project is connected to your Vercel Project. You can then use Azure Pipelines inside your Azure DevOps project to trigger a Vercel Deployment.
This page will help you use the extension in your own use case. You can:
- Follow the quickstart to set up the extension and trigger a production deployment based on commits to the
mainbranch - Use the full-featured pipeline for a similar setup as Vercel's other git integrations. This includes preview deployment creation on pull requests and production deployments on merging to the
mainbranch - Review the extension task reference to customize the pipeline for your specific use case
At the end of this quickstart, your Azure Pipelines will trigger a Vercel production deployment whenever you commit a change to the main branch of your code. To get this done, we will follow these steps:
- Create a Vercel Personal Access Token
- Create secret variables
- Set up the Vercel Deployment Extension from the Visual Studio marketplace
- Set up a basic pipeline in Azure Pipelines to trigger production deployments on Vercel
- Test your workflow
Once you have the Vercel Deployment extension set up, you only need to modify your pipeline (Steps 4 and 5) to change the deployment workflow to fit your use case.
An empty Vercel Project with no Git integration
An Azure DevOps project that contains the code that you would like to deploy on Vercel
To create an empty Vercel project:
- Use the Vercel CLI with the
addcommand
vercel project add- Or through the dashboard and then disconnect the Git integration that you would have set up
- Follow Creating an Access Token to create an access token with the scope of access set to the team where your Vercel Project is located
- Copy this token to a secure location
For security purposes, you should use the above created token in your Azure Pipeline through secret variables.
- For this quickstart, we will create the secret variables when we create the pipeline. Once created, these variables will always be accessible to that pipeline
- Otherwise, you can create them before you create the pipeline in a variable group or in Azure Key Vault as long as you make sure that your Azure Project has the right access
- Go to the Vercel Deployment Extension Visual Studio marketplace page
- Click Get it free and select the Azure DevOps organization where your Azure Project is located
This step assumes that your code exists as a repository in Azure Repos and that your Vercel Project is named
azure-devops-extension.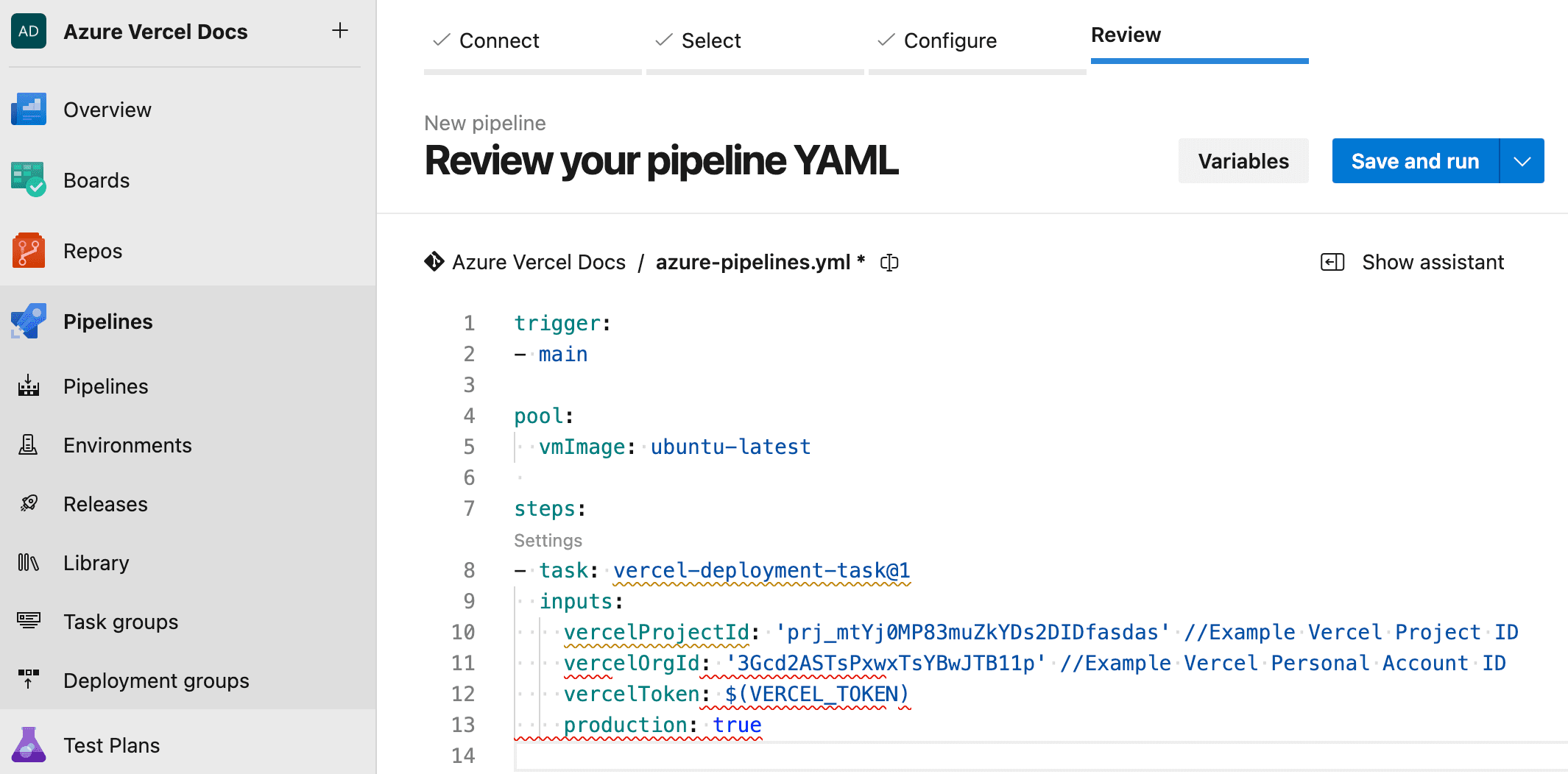
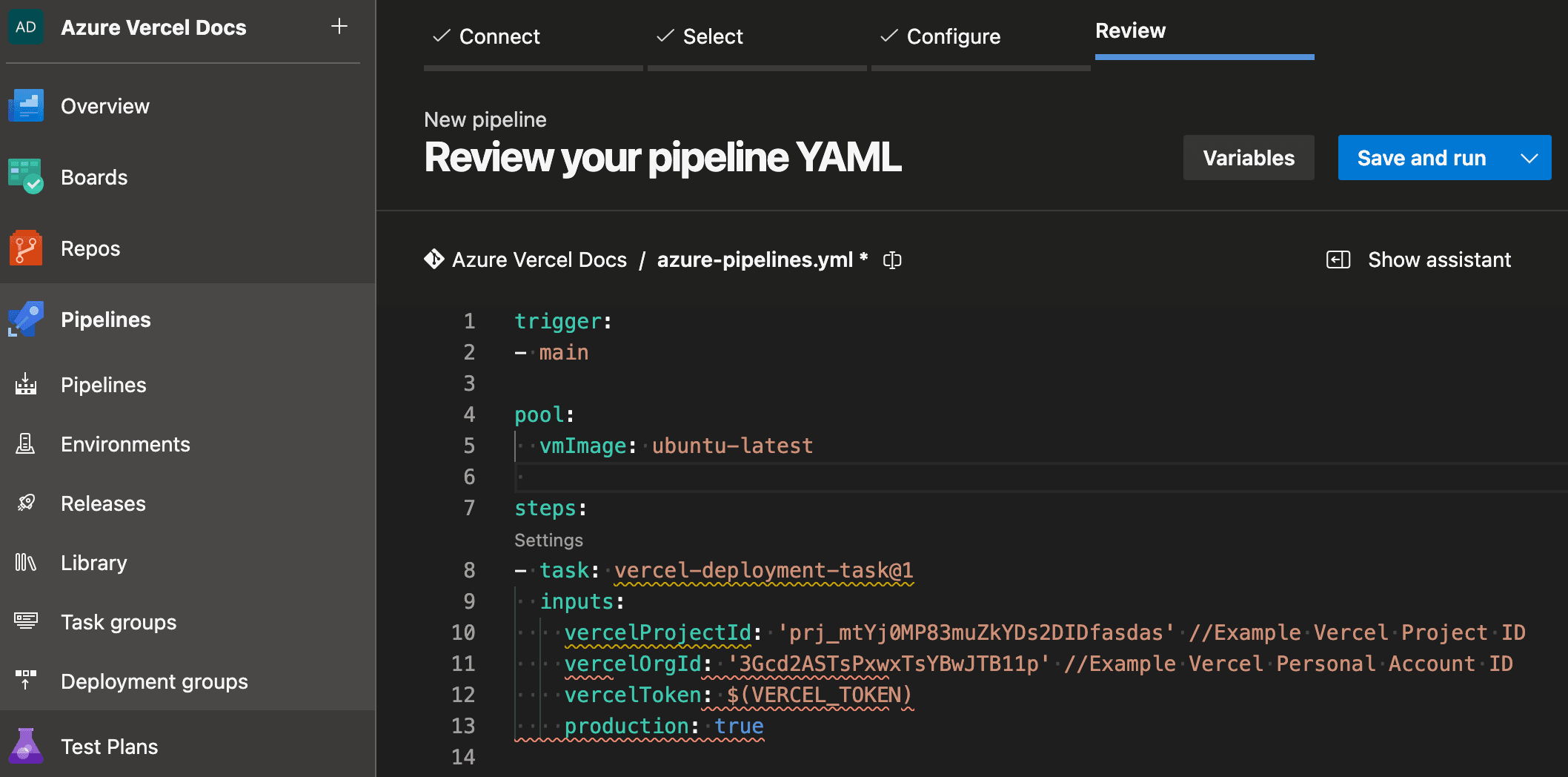
Azure Pipelines creation at the review stage to create variables and save/edit your pipeline - From the Azure DevOps portal, select Pipelines from the left side bar
- Select the New Pipeline button
- Select where your code is located. In this example, we uploaded the code as an Azure Repos Git: select Azure Repos Git and then select your uploaded repository.
- Select Starter template for the pipeline configuration
- In the Review your pipeline YAML step, select Variables on the top right
- Select New Variable, use
VERCEL_TOKENas the name and the value of the Vercel Personal Access Token you created earlier. Check the secret option. Select Ok
- Select New Variable, use
- Close the Variables window and paste the following code to replace the code in
azure-pipelines.yml, that you can rename tovercel-pipeline.yml
vercel-pipeline.ymltrigger: - main pool: vmImage: ubuntu-latest steps: - task: vercel-deployment-task@3 inputs: vercelProjectId: 'prj_mtYj0MP83muZkYDs2DIDfasdas' # Example Vercel Project ID vercelTeamId: 'team_ZWx5eW91dGh0b25BvcnRhbnRlYn' # Example Vercel Team ID vercelToken: $(VERCEL_TOKEN) production: trueLook for Project ID located on the Vercel Project's Settings page at Project Settings > General.
- If your Project is located under your Hobby team, look for Your ID under your Vercel Personal Account Settings
- If your Project is located under a Team, look for Team ID under Team Settings > General
- Select Save and Run
- This should trigger a production deployment in your Vercel Project as no code was committed before
- Make a change in your code inside Azure Repos from the
mainbranch and commit the change - This should trigger another deployment in your Vercel Project
- Make a change in your code inside Azure Repos from the
Your Azure DevOps project is now connected to your Vercel project with automatic production deployments on the main branch. You can update or create pipelines in the Azure DevOps project to customize the Vercel deployment behavior by using the options of the Vercel Deployment Extension.
In a production environment, you will often want the following to happen:
- Trigger preview deployments for pull requests to the
mainbranch - Trigger production deployments only for commits to the
mainbranch
Before you update your pipeline file to enable preview deployments, you need to configure Azure DevOps with pull requests.
In order to allow pull requests in Azure Repos to create a deployment and report back with a comment, you need the following:
- An Azure DevOps Personal Access Token
- A build validation policy for your branch
- Go to your Azure DevOps account and select the user settings icon on the top right
- Select Personal access tokens from the menu option
- Select the New Token button
- After completing the basic token information such as Name, Organization, and Expiration, select the Custom defined option under Scopes
- At the bottom of the form, select Show all scopes
- Browse down the scopes list until Pull Request Threads. Select the Read & Write checkbox
- Select Create at the bottom of the form
- Make sure you copy the token to a secure location before you close the prompt
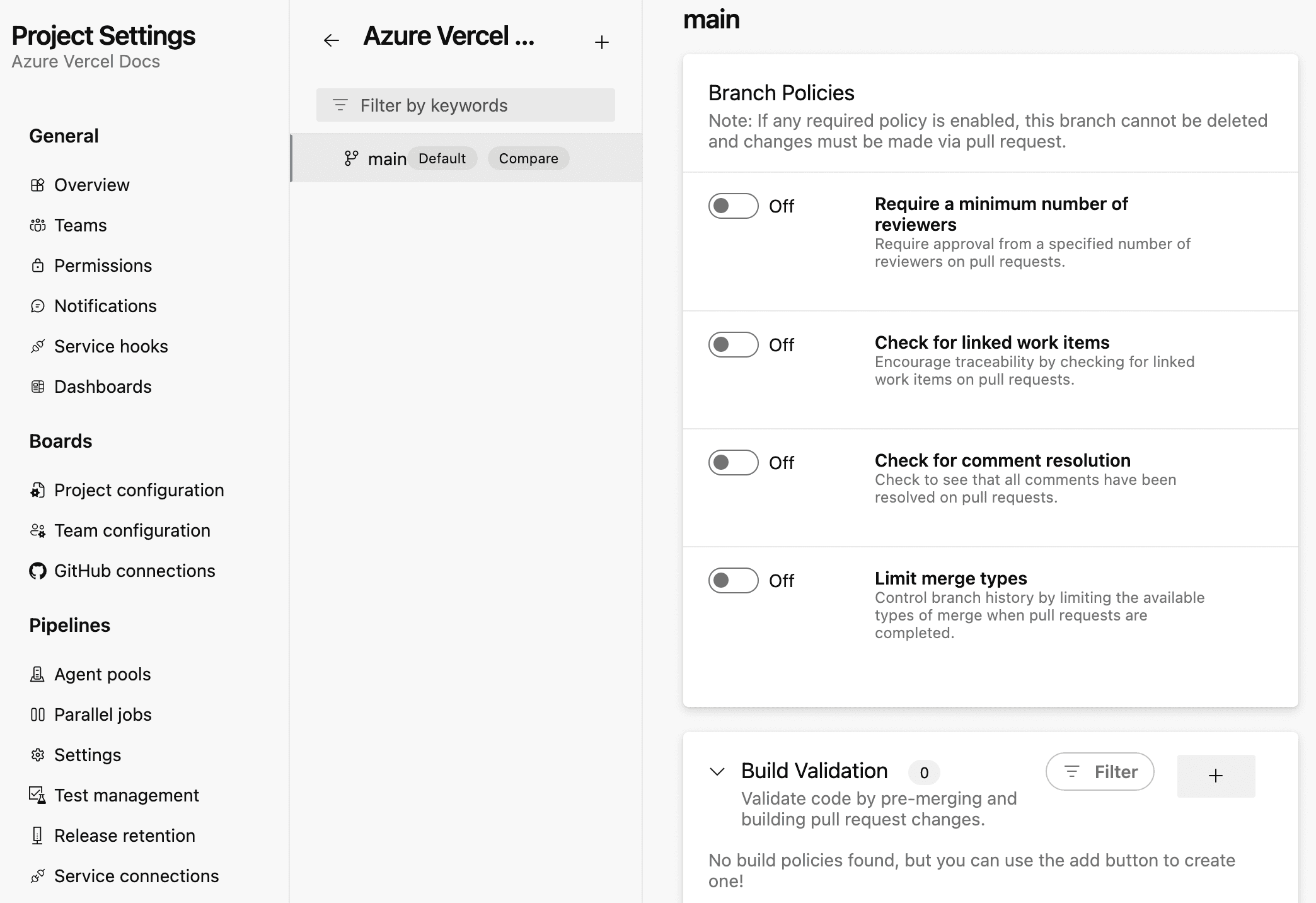
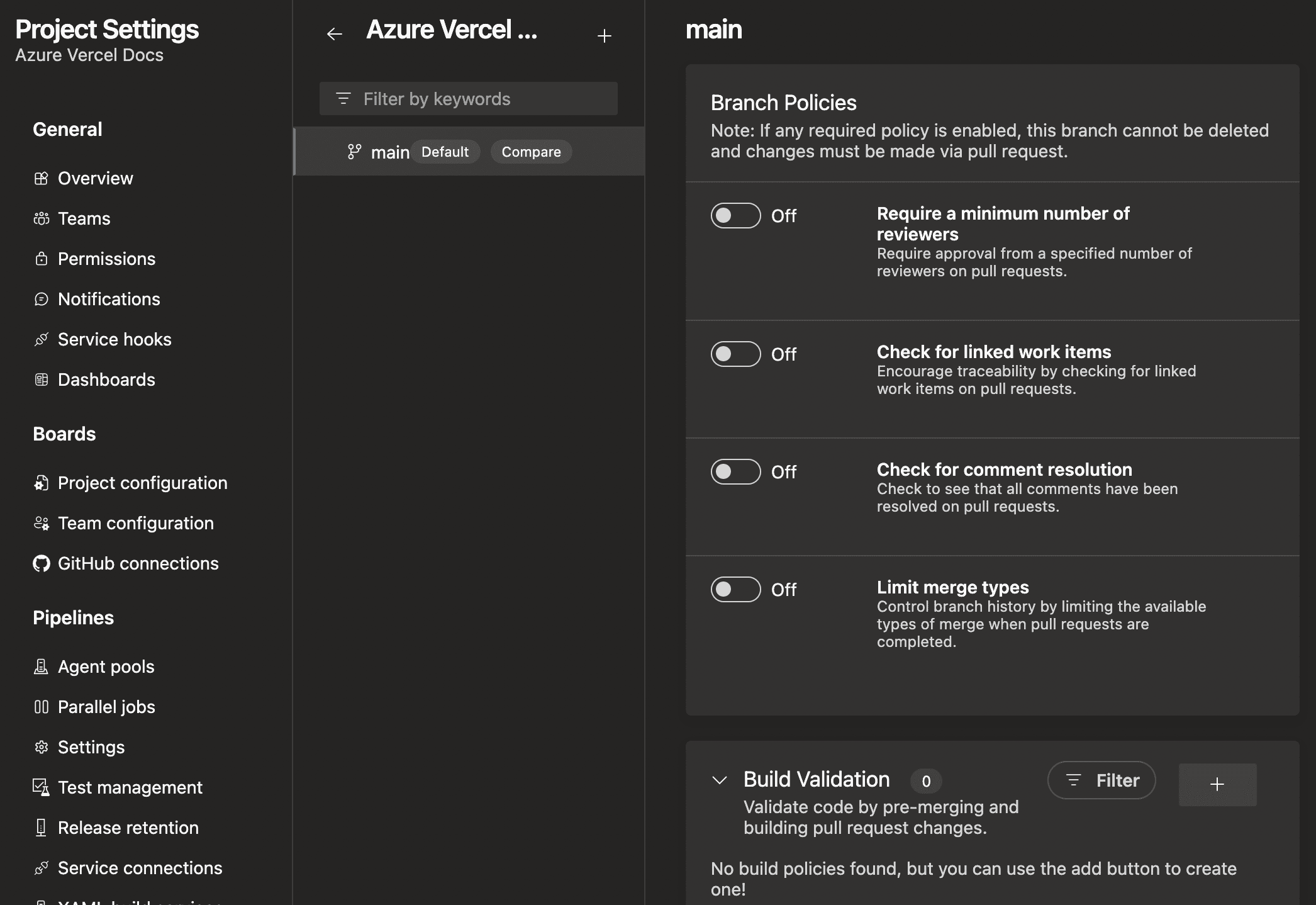
- Go to your Azure DevOps Project's page
- Select Project settings in the lower left corner
- From the Project settings left side bar, select Repositories under Repos
- Select the repository where your vercel pipeline is set up
- Select the Policies tab on the right side
- Scroll down to Branch Policies, and select the
mainbranch - Scroll down to Build Validation and select on the + button to create a new validation policy
- Select the pipeline you created earlier and keep the policy marked as Required so that commits directly to main are prevented
- Select Save
Create a pull request to the main branch. This will trigger the pipeline, run the deployment and comment back on the pull request with the deployment URL.
- From your Azure DevOps Project, select Pipelines from the left side bar
- Select the pipeline that you want to edit by selecting the icon
- Select the Variables button and add a new secret variable called
AZURE_TOKENwith the value of the Azure DevOps Personal Access Token you created earlier. Select Ok - Close the Variables window and paste the following code to replace the code in
vercel-pipelines.yml
trigger:
- main
pool:
vmImage: ubuntu-latest
variables:
isMain: $[eq(variables['Build.SourceBranch'], 'refs/heads/main')]
isPR: $[eq(variables['Build.Reason'], 'PullRequest')]
steps:
- task: vercel-deployment-task@3
name: 'Deploy'
condition: or(eq(variables.isMain, true), eq(variables.isPR, true))
inputs:
vercelProjectId: 'prj_mtYj0MP83muZkYDs2DIDfasdas' # Example Vercel Project ID
vercelTeamId: 'team_ZWx5eW91dGh0b25BvcnRhbnRlYn' # Example Vercel Team ID
vercelToken: $(VERCEL_TOKEN)
production: $(isMain)
- task: vercel-azdo-pr-comment-task@3
condition: eq(variables.isPR, true)
inputs:
azureToken: $(AZURE_TOKEN)
deploymentTaskMessage: $(Deploy.deploymentTaskMessage)- Select Save
The vercel-deployment-task creates an output
variable
called deploymentTaskMessage. By setting the name: of the step to
'Deploy', you can access it using $(Deploy.deploymentTaskMessage) which
you can then assign to the input option deploymentTaskMessage of the
vercel-azdo-pr-comment-task task step.
- Create a new branch in your Git repository in Azure Repos and push a commit
- Open a pull request against the
mainbranch - This will trigger a pipeline execution and create a preview deployment on Vercel
- Once the deployment has completed, you will see a comment on the pull request in Azure DevOps with the preview URL
Here, you can find a list of available properties for each of the available tasks in the Vercel Deployment Extension.
| Property | Required | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
vercelProjectId | No | string | The ID of your Vercel Project; starts with project_. It can alternatively be set as the environment variable VERCEL_PROJECT_ID |
vercelTeamId | No | string | The ID of your Vercel Team; starts with team_. It can alternatively be set as the environment variable VERCEL_TEAM_ID |
vercelToken | No | string | A Vercel personal access token with deploy permissions for your Vercel Project. It can alternatively be set as the environment variable VERCEL_TOKEN |
vercelCWD | No | string | The working directory where the Vercel deployment task will run. When omitted, the task will run in the current directory (default value is System.DefaultWorkingDirectory). It can alternatively be set as the environment variable VERCEL_CWD |
production | No | boolean | Boolean value specifying if the task should create a production deployment. When omitted or set to false, the task will create preview deployments |
target | No | string | Option to define the environment you want to deploy to. This could be production, preview, or a custom environment. This is equivalent to passing the --environment when deploying using the Vercel CLI. |
archive | No | boolean | Enables the --archive=tgz flag for the internal Vercel CLI operations |
env | No | string | Adding environment variables at runtime using the Vercel CLI's --env option |
buildEnv | No | string | Adding build environment variables to the build step using the Vercel CLI's --build-env option |
debug | No | boolean | Boolean value that enables the --debug option for the internal Vercel CLI operations |
logs | No | boolean | Boolean value that enables the --logs option for the internal Vercel CLI operations |
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
deploymentTaskMessage | string | The message output taken from the deployment; can be passed to Vercel Azure DevOps Pull Request Comment Task |
deploymentURL | string | The URL of the deployment |
originalDeploymentURL | string | Original URL of the deployment; can be used to create your own alias in a depending separate task |
| Property | Required | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
azureToken | Yes | string | An Azure Personal Access Token with the PullRequestContribute permission for your Azure DevOps Organization |
deploymentTaskMessage | Yes | string | The message that will added as a comment on the pull request. It is normally created by the Vercel Deployment Task |
Was this helpful?

