3 min read
We've encapsulated 10+ years of React and Next.js optimization knowledge into react-best-practices, a structured repository optimized for AI agents and LLMs.


React performance work is usually, well, reactive. A release goes out, the app feels slower, and the team starts chasing symptoms. That’s expensive, and it’s easy to optimize the wrong thing.
We’ve seen the same root causes across production codebases for more than a decade:
Async work that accidentally becomes sequential
Large client bundles that grow over time
Components that re-render more than they need to
The “why” here is simple: these aren’t micro-optimizations. They show up as waiting time, jank, and repeat costs that hit every user session.
So, we put together this React best practices framework to make those problems easier to spot and faster to fix.
Link to headingThe core idea: ordering
Most performance work fails because it starts too low in the stack.
If a request waterfall adds 600ms of waiting time, it doesn’t matter how optimized your useMemo calls are. If you ship an extra 300KB of JavaScript on every page, shaving a few microseconds off a loop won’t matter.
Performance work also compounds. A small regression you ship today becomes a long-term tax on every session until someone pays down the debt.
So the framework starts with the two fixes that usually move real-world metrics first:
Eliminate waterfalls
Reduce bundle size
Then it moves on to server-side performance, client-side fetching, and re-render optimization.
It includes 40+ rules across 8 categories, ordered by impact, from CRITICAL (eliminating waterfalls, reducing bundle size) to incremental (advanced patterns).
Link to headingWhat else is inside?
The repository covers eight performance categories:
Eliminating async waterfalls
Bundle size optimization
Server-side performance
Client-side data fetching
Re-render optimization
Rendering performance
Advanced patterns
JavaScript performance
Each rule includes an impact rating (CRITICAL to LOW) to help prioritize fixes, plus code examples showing what breaks and how to fix it.
For example, here’s a common pattern that blocks unused code:
Incorrect (blocks both branches):
async function handleRequest(userId: string, skipProcessing: boolean) { const userData = await fetchUserData(userId) if (skipProcessing) { // Returns immediately but still waited for userData return { skipped: true } } // Only this branch uses userData return processUserData(userData)}Correct (only blocks when needed):
async function handleRequest( userId: string, skipProcessing: boolean) { if (skipProcessing) { return { skipped: true } }
const userData = await fetchUserData(userId) return processUserData(userData)}
Individual rule files compile into AGENTS.md, a single document that your agents can query when reviewing code or suggesting optimizations. It’s designed to be followed consistently, including by AI agents doing refactors, so teams can apply the same decisions across a large codebase.
Link to headingHow these practices were collected
These aren’t theoretical. They come from real performance work on production codebases.
A few examples:
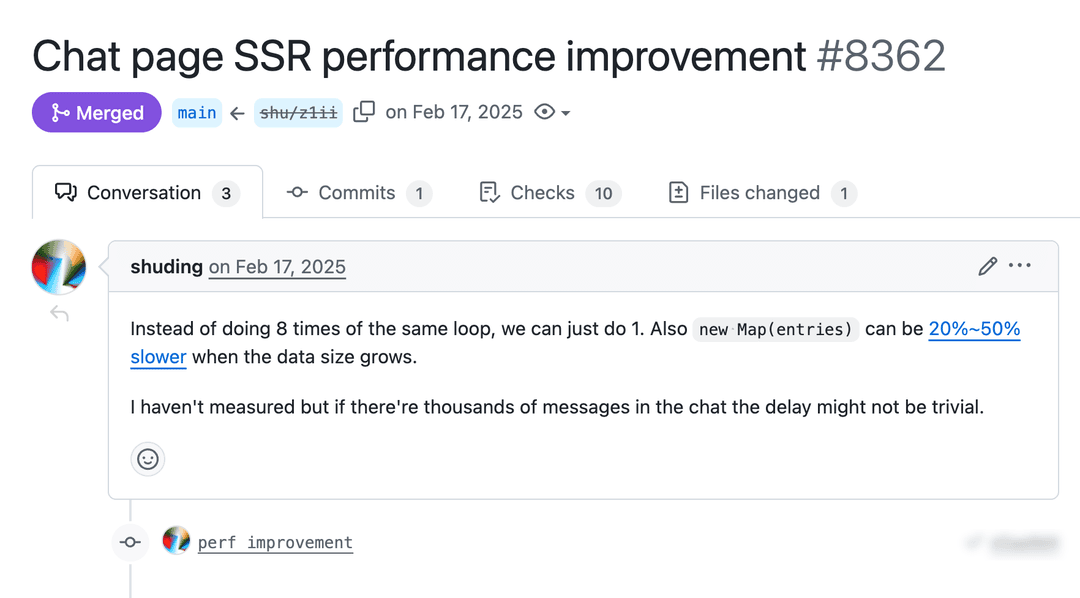
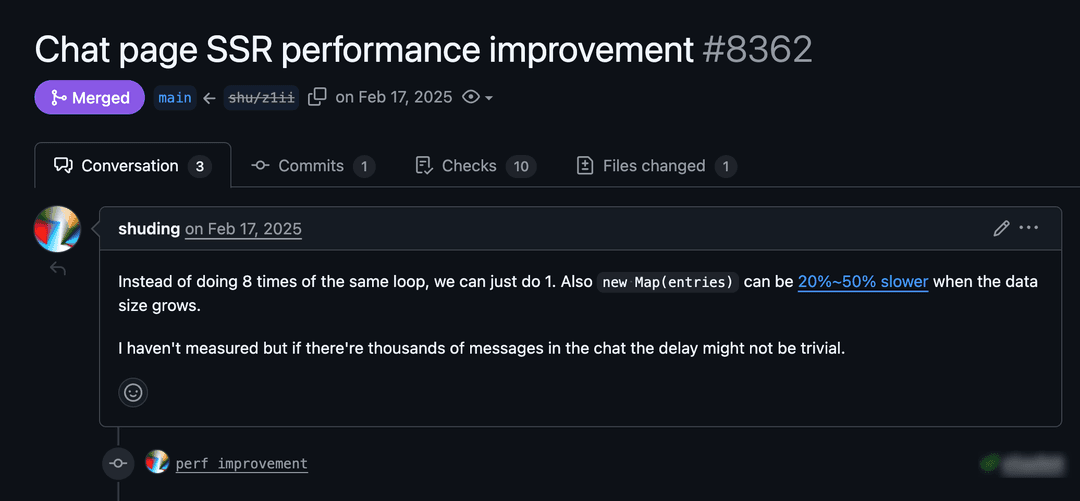
Combining loop iterations
A chat page was scanning the same list of messages eight separate times. We combined it into a single pass, which adds up when you have thousands of messages.
Parallelizing awaits
An API was waiting for one database call to finish before starting the next, even though they didn’t depend on each other. Running them at the same time cut the total wait in half.
Lazy State Initialization
A component was parsing a JSON config from localStorage on every render, even though it only needed it once for state initialization. Wrapping the it in a callback (useState(() => JSON.parse(...))) eliminated wasted work.
Link to headingUsing react-best-practices in your coding agent
These best practices are also packaged up as Agent Skills that install into Opencode, Codex, Claude Code, Cursor, and other coding agents. When your agent spots cascading useEffect calls or heavy client-side imports, it can reference these patterns and suggest fixes.
npx skills add vercel-labs/agent-skillsCheck out the react-best-practices repository.